Welcome to Part 2 of our guide on investing in ETFs and index funds for beginners. In Part 1, we covered the basics of stock valuation and the differences between active and passive investing strategies. Now, in this article, we’ll dive deeper into the practical aspects of managing your portfolio, such as how to invest using ETFs and index funds, the importance of diversification, and how to manage investment fees and risks. Let’s explore these key components that will help you strengthen your investment strategy and achieve long-term success.
Table of Contents
ToggleIndex Funds and ETFs:
For beginners, ETFs and index funds are great starting points because they offer low-cost diversification across many companies. They are easy to navigate and can generate significant returns without much effort.
What is an ETF?
An Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF) lets you buy many stocks simultaneously. When you purchase shares of ETFs, your funds will be invested proportionately based on the set investment objective.
ETFs are of two basic types: Passive ETFs and Active ETFs.
While Passive ETFs track a stock index, Active ETFs involve more detailed portfolio management.
Index ETFs track a specific market index’s performance to replicate that target index’s performance.
Although similar, the significant difference between ETFs and Index Funds is in their manner of sales and purchases.
Key Benefits of Investing in ETFs and Index Funds for Beginners
- ETFs can be traded anytime during the day on the stock market.
- Index funds can only be bought and sold at the end of the trading day based on the fund’s net asset value.
- While index funds have a minimum investment requirement, ETFs don’t.
Actionable Step: Consider exploring popular ETFs and Index Funds on platforms like Vanguard or BlackRock to see what aligns with your investment goals.
Diversification is Key
Diversification of investments is recommended for all investors. Financial advisors suggest building a mixed-stock investment portfolio for reduced risk and more growth opportunities.
A diversified portfolio can include stocks across the tech, healthcare, energy, and consumer goods sectors. When you invest in several high-quality companies, you can achieve a diversified portfolio.
For more about stock diversification, check out our detailed guide here.
Understanding Fees and Costs
It’s easy to overlook investment charges as a beginner investor, but these can significantly impact your overall investment returns. Here are some fees and costs to be aware of:
Investment Fees to Watch Out For:
- Platform management fees: Often charged as a percentage of your portfolio value.
- Platform transaction charges: Fees for buying or selling shares.
- Dividend reinvestment fees: Some platforms charge when you reinvest dividends.
- Fund fees: Managed funds usually have higher fees than index funds.
Actionable Tip: The effect of compounding fees over time can significantly reduce your investment returns. For example, if your portfolio grows by 5% but incurs 2% in fees, you only see a 3% return. Over 10 years, this compounded effect can reduce the growth of your investments. Keep an eye on fees to maximise returns.
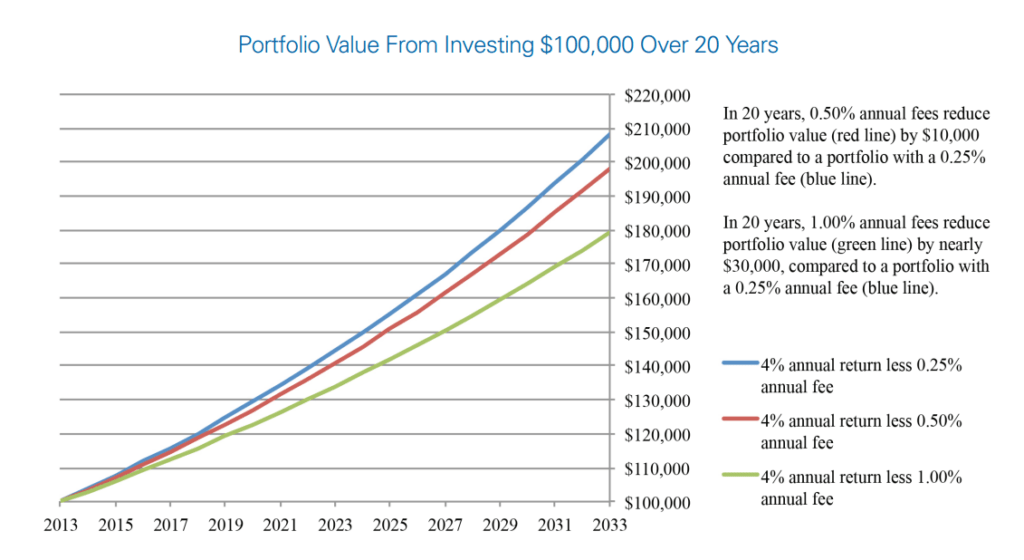
Types of Investment Risks
All investments come with risk, and stock investments are no different. Understanding the types of risks involved can help you make better, more informed decisions.
- Market Risk: Prices fall when the stock market declines, especially during economic recessions.
- Inflation Risk: If inflation outpaces your investment growth, the value of your money decreases.
- Company-Specific Risks: Risks arising from internal company issues or external events affecting the company.
How Much Risk Is Right for Me?
When it comes to determining your risk tolerance, it’s a personal choice that depends on your financial goals and timeline. While a global tracker fund provides broad exposure, it’s essential to ask yourself: How much risk are you willing to accept in pursuit of higher returns? Please take a look at the investment mix and allocate accordingly.
Past performance should not be seen as an indication of future performance. While past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance, history suggests that the longer you invest, the lower your chances of experiencing negative returns. For further guidance, read more on the Principles of Investing.
Managing Investment Risk
Building a stock portfolio for beginners means considering diversification—spreading your investments across different sectors and regions to reduce risk. Spread your investments across various asset types (e.g., stocks, bonds, real estate), sectors, and regions. While some investments may underperform, others will balance it out.
Actionable Step: Look into building a diversified portfolio by investing in ETFs, Index Funds, and stocks from various industries.
Tracking Your Investments
Once you’ve made your investments, tracking their performance regularly is essential to ensure they align with your financial goals.
Reviewing Your Portfolio:
Experts suggest reviewing your portfolio at least twice a year. This helps keep your investments on track.
Rebalancing Your Portfolio:
Rebalancing ensures that your portfolio aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. If some stocks perform better than others, you can buy more of the better-performing ones or sell off underperforming stocks.
Balancing Global Exposure in Your Portfolio
When constructing a diversified portfolio, it’s crucial to consider the sectors and industries you’re investing in and the geographical exposure of your assets. If you’re unsure about achieving the right balance, looking at the relative size of global stock markets can give you a clearer idea.
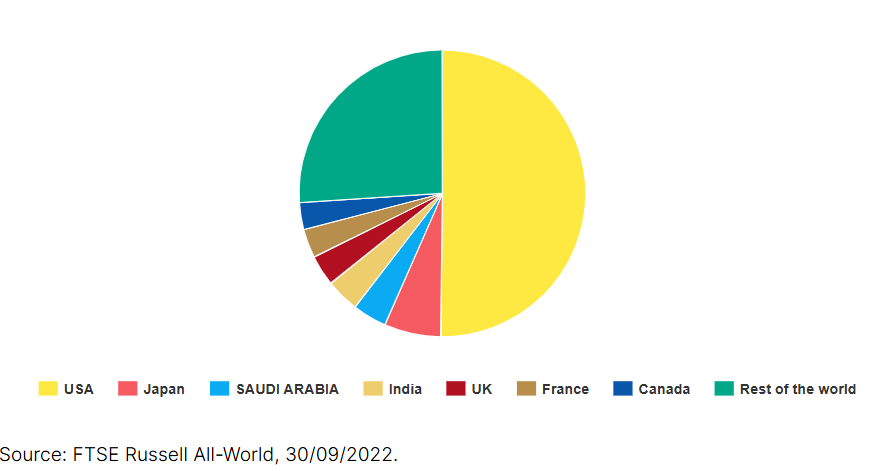
For example, the US markets represent the most significant portion of global markets, making up over 50%. This includes major exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the S&P 500. In comparison, the UK only accounts for approximately 4%. While these figures may evolve as markets grow at different rates, it’s essential to consider when deciding how to allocate assets in your portfolio.
This global market breakdown can be a helpful benchmark when deciding how much to allocate to different regions. A well-diversified portfolio should be spread across various international markets, reducing risk and boosting potential returns.
At the core of your portfolio, selecting funds offering broad exposure is vital. For example, investing in developing countries in Asia and emerging markets can be riskier than investing in more stable markets like the US or UK. To balance this risk, consider including a global tracker fund, which provides exposure to stock markets worldwide with a single investment.
However, remember that global tracker funds focus on tracking an index and typically invest in shares. This means they won’t offer diversification across other asset classes, such as bonds or commodities. To add stability, consider incorporating multi-asset funds, which include a mix of different investment types.
Using Additional Tools and Resources
When it comes to investing in ETFs and index funds for beginners, these tools provide a simple way to diversify your portfolio and grow your wealth.
Here are some of our recommendations for UK investors:
Actionable Step: Explore beginner-friendly investing resources for ongoing education.
When to Seek Financial Advisors and Guidance
How do you know if you need a financial advisor?
- If your investment isn’t growing as expected.
- If you’re too busy to manage your investments.
- If your portfolio needs a professional review.
At KIAS Consulting Pro, we offer professional guidance and support for investors in the UK. Contact us for a free initial consultation, and let us help you start your investment journey!
Disclosure:
The information provided in this article is solely to enable you to make your own investment decisions. The investments and/or services referred to may not be suitable for all investors. You are responsible for making your own investment decisions. Unlike cash, stock market-based investments are not guaranteed and may fall in value and rise. Therefore, we recommend investing for the long term (5+ years) to increase your chances of achieving positive returns. Ultimately, you could get back less than you invest. Any yields or returns will vary, and income is variable and not guaranteed.
Past performance should not be seen as an indication of future performance. While past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance, history suggests that the longer you invest, the lower your chances of experiencing negative returns.
There’s no better time to start investing than now! If you need help navigating the stock market or are ready to start investing in a tax-efficient account, please get in touch with us or explore more articles on our blog to help you on your investment journey.
Next Steps: Start Building Your Stock Portfolio with Confidence
Now that you’ve learned about diversification, fees, and managing risks, it’s time to start tracking your investments and regularly reviewing your portfolio. If you’re feeling overwhelmed or need help getting started with your stock portfolio, contact us for a free initial consultation. Let us guide you through the process and help you make confident decisions.
Book your free consultation now





Thanks for one’s marvelous posting! I truly enjoyed reading it, you are a great author.I will ensure that I bookmark your blog and will often come back in the future.I want to encourage you to definitely continue your great posts, have a nice day!
Thank you so much for your kind words. I truly appreciate you taking the time to read the post and share your feedback. It means a lot to know that you found it helpful and enjoyable.
I’m glad you found the content valuable, and I look forward to continuing to share practical insights to help you build and manage your investments with confidence. Please feel free to explore the rest of the blog, especially the other parts of the portfolio-building series, as they’re designed to guide you step-by-step.
Wishing you every success on your investing journey, and I hope to see you here again soon!